Polymyositis
About Polymyositis
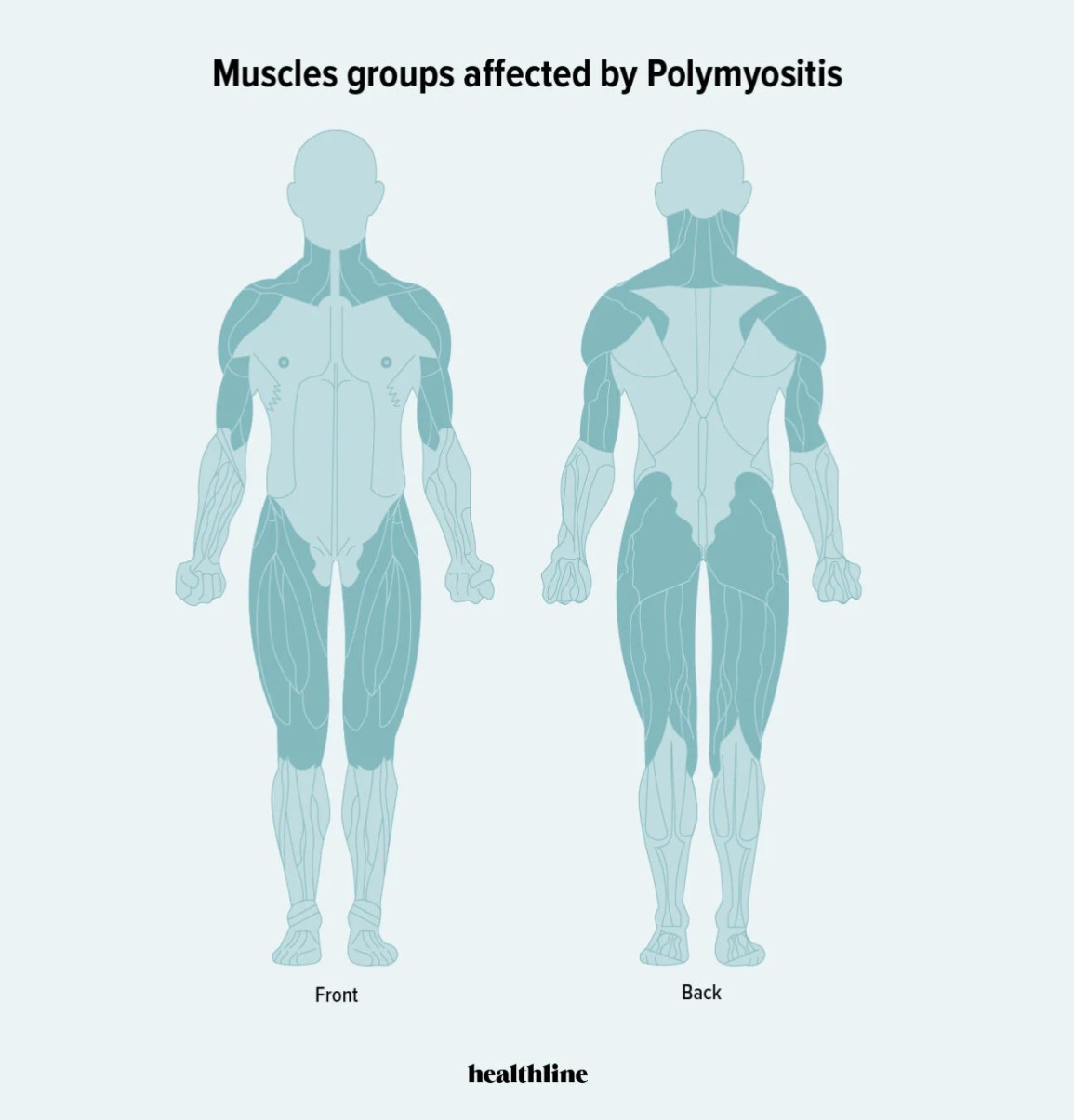
Polymyositis (PM) is more commonly found in adult women than men
It typically causes muscle weakness which develops gradually over time, starting with the muscles near the trunk of the body such as the neck, hips, back, and shoulders. Some people with PM may experience muscle pain, difficulty breathing, and swallowing.
Elevated levels of creatine kinase (CK) in the blood, which indicate muscle damage, are commonly seen in PM patients and reflect the degree of muscle inflammation. Like dermatomyositis (DM), PM in adults can be associated with other autoimmune diseases. PM can be misdiagnosed as necrotizing myopathy (NM) or sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM) if muscle biopsy results are inconclusive or not performed.
What are symptoms of Polymyositis?
Polymyositis is a rare autoimmune disease that affects the skeletal muscles, causing inflammation and progressive muscle weakness. The symptoms of polymyositis can vary widely, but some common ones include:
- Muscle weakness: This is the most common symptom of dermatomyositis and can affect any muscle group, but usually affects the proximal muscles (hips, shoulders, neck).
- Skin rash: A characteristic rash on the face, chest, back, hands, and/or elbows is a common symptom of dermatomyositis. The rash often appears before the muscle weakness.
- Difficulty swallowing: This can occur if the muscles responsible for swallowing are affected.
- Fatigue: Many people with dermatomyositis experience extreme fatigue and weakness, even with minimal activity.
- Joint pain: Joint pain and stiffness may be present, especially in the morning.
- Shortness of breath: This can occur if the muscles responsible for breathing are affected.
- Raynaud's phenomenon: This is a condition in which the fingers or toes turn white or blue in response to cold or stress.
